Acute epiglottitis is a common cause of severe sore throat and feeding difficulty in children mostly in between 2-6 years of age. It is an acute inflammation and edema of the supraglottitis mainly the epiglottitis, confined to supraglottic structure, Epiglottis, Aryepiglottic folds and Arytenoid region
It may also can occur in adult. It is an laryngeal infections. So at first you need to know some thing about larynx. I am going to tell you about that in short. Its incidence has decreased dramatically because of Vaccine. It is sometimes termed as supraglottitis.
Anatomy of Larynx:

The Larynx is an apparatus which guards the entrance to the lower tract airway and houses the vocal cords. It is comprises of cartilage, ligaments, muscles and mucous membrane. There are 3 paired and 3 unpaired cartilages. Epiglottis is one of them, unpaired cartilages placed at the above. Cricoid cartilage is that thing that we can feel in touching the throat, it is actually a prominence in your front of throat. The main part of the laryngeal framework is formed by the thyroid cartilages. The epiglottitis is attached to the thyroid prominence at the level of vocal cords.
The Total larynx is divided into three part for the purpose of laryngeal cancer treatment.
- Supraglottis: The supraglottic area includes the epiglottis, the aryepiglottic folds, the false vocal cords, arytenoids and the ventricles.
- Glottis
- Subglottis
The epiglottis is usually crisp and whitish. An erythematous, edematous epiglottis may indicate epiglottitis.
What Causes Epiglottitis:
Hemophilus influenzae type B (HIB) is the most common bacteria that cause this. Others are beta hemolytic streptococci, pneumococci and staphylococcus which may be the reason of acute epiglottitis.
How to Identify (Symptoms):
The onset of supraglottitis is acute, often in as little as 2 to 6 hour. The symptomes are listed below:
- Severer sore throat.
- Dribbling of saliva.
- High rise of temperature.
- Inspiratory stridor. Sits upright with greater inspiratory than expiratory stridor.
- Muffled voice or commonly known as Hot Potato voice.
- Flushed face.
- Toxic looking.
Stridor: It is noisy breathing due to partial airway obstruction at or below the level of larynx. Laryngeal stridor is always inspiratory. Bronchial asthma also causes stridor but is is Expiratory.
How To Diagnose?
Diagnosis is mainly done on the basis on History given by the parents and by looking at the child. Somehow to confirm the diagnosis Direct Laryngoscopy can be done at Operation Theaters by Expert anesthetist and facility for pediatric intubation should be available.
A lateral extended soft-tissue radiography is often diagnostic. It may show swollen epiglottis as thump sign but may be dangerous to do in children. On the direct Laryngoscopy it shows edematous aryepiglottic folds and a red cherry epiglottis. It is the most impressive feature.
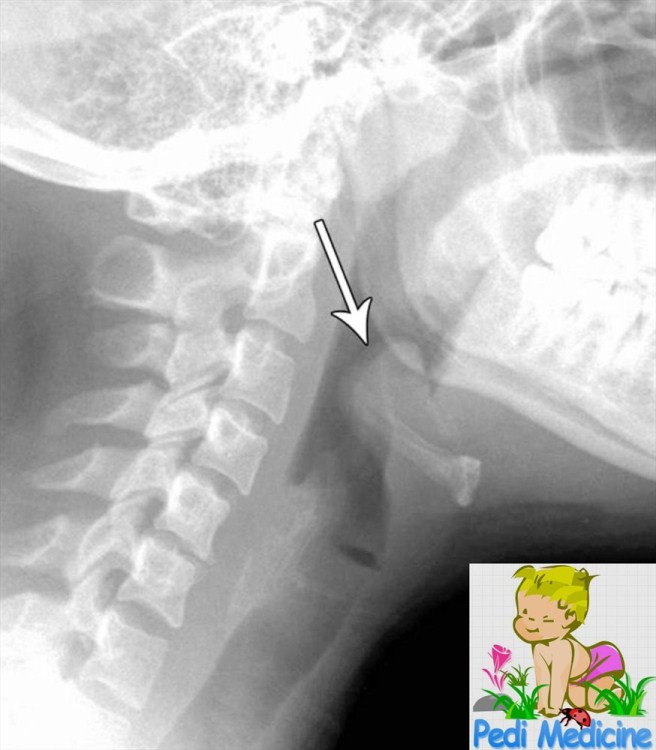
Respiratory obstruction is probably caused by at least two factors: (1) a swollen epiglottis and arytenoepliglottic fold with supraglottic narrowing and (2) excessive, thick, tenacious oral and pharyngeal secretions, which accumulate because of odynophagia. A swab may taken and blood culture can be done for antibiotic sensitivity.
Other Disease that may Mistaken with Epiglottitis:
Croup also known as Acute Laryngo-Traceo-Bronchitis has the same feature like as epiglottis. But it can be easily distinguishable. The child with epiglottitis classically appears with a 2- to 6-hour history of stridor, sitting upright, and drooling.
The child with croup has a several-day history of prodromal symptoms with worsening stridor and a seal-like (croupy) cough. Croup is common in between 6 month to 3 years.
Treatment of Acute Epiglottitis:
The treatment is simple. Antibiotics is the cure. Some prefers Chloramphenicol as 30%Hemophilus influenzae is resistant to ampicillin. Cefuroxime is now the drug of choice for supraglottitis at several large institutions. It has excellent bactericidal activity against most gram-positive bacteria and most gram-negative bacteria, including all strains of H. influenza. In addition, it has adequate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) penetration and a high margin of safety.
An alternative drug is ceftriaxone. Some clinicians prefer ceftriaxone to cefuroxime because of its less-frequent dosing schedule. But it vary in countries and the choice of doctor.
Supportive therapy should taken care of. As there is airway obstruction, Tracheostomy or Intubation may be needed. Severe ill child should transfer to ICU. In the most recent large study, 94% of children admitted with epiglottitis were intubated, 6% were observed in the ICU while breathing spontaneously, and none underwent tracheostomy. Intubation is usually maintained for 24 to 48 hours
Advice for parents:
If you find these symptoms, urgent call for Doctor. There are also vaccine available to prevent the infection. HIB vaccine 3 doses is given at 2,3 and 4th Month of your child for prevention of Epiglottis and Meningitis.

Very much informative and the image is really great!
Thanks for your Inspiration, i appreciate that.