Ectodermal Dysplasia is a rare group of genetic disorders. It is derived from the abnormalities of development from ectodermal structures. It may be autosomal dominant or recessive. Diagnosis is made based on clinical evaluation. Ectodermal dysplasias are described as “heritable conditions in which there are abnormalities of two or more ectodermal structures such as the hair, teeth, nails, sweat glands, salivary glands, cranial-facial structure, digits and other parts of the body.” There are many types of genetic causes. For example, Hay–Wells syndrome and EEC syndrome are all associated with TP63 and Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia can be associated with EDA, EDAR and EDARADD. Treatment is mainly symptomaSummaryse summary
Tasin 7-Year-old immunized boy hailing from Gazipur admitted with the complaints of
- Inability to take solid food due to delayed dentition
- Less hair growth since birth
- Heat intolerance since 2 years of age
According to the statement of informant mother, her child had a history of delayed dentition as 1st teeth erupted at 5 years of age which was followed by the inability to eat solid foods. On query mother also gave a history of heat intolerance since 2 years of age and no sweat production at all for which she had to take bath several times a day. He also had sparse slowly growing scalp hair since birth. He had a history of frequent fever since early infancy, especially during hot weather. There was no history of prematurity, inadequate sun exposure, diarrhea, or malabsorption. Now he got admitted to BSMMU for further evaluation and management.
He was delivered by LUCS at term with average birth weight and cried immediately after birth. During birth, he had no eyebrows and eyelashes, and his nails were absent. Tasin had only scanty hair on his scalp. He is developmentally age-appropriate. The child had a history of frequent fever since early infancy, especially during hot weather.
On General Examination:
- Appearance: Well Alert, mildly pale
- Facies: Depressed nasal bridge, thick – Everted lips, Low set ears.
- Eye: Eyebrows and lashes –sparse
- Oral cavity: Oligodontia ( only 4 teeth in upper jaw-2 incisors and 2 molars)
- Skin survey: Skin dry, blackish discoloration present in the periorbital area, multiple hyperpigmented lesions over the forearm and scalp.
- Hair: Sparse, fine, and lightly pigmented.
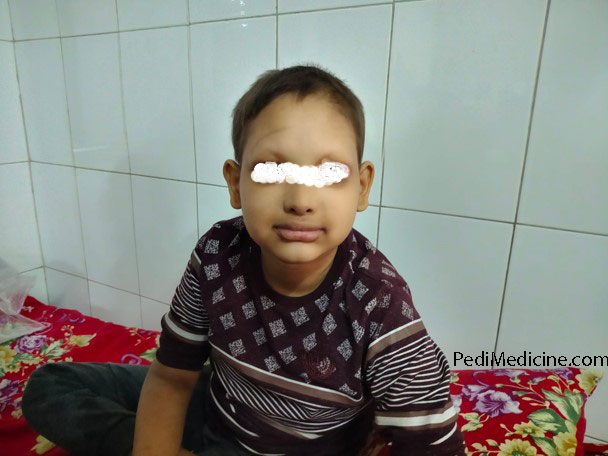
(Only Positive findings are mentioned)
Anthropometrically he is well thriving. On systemic examination, revealed no abnormality.
So our provisional diagnosis was Ectodermal dysplasia most probably Hypohydrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia.



Points in favour of ectodermal dysplasia:
- Teeth: Oligodontia
- Facies: Depressed nasal bridge, thick-everted lips
- Hair: Sparse, lightly hypopigmented poor growing hair
- Skin: Heat intolerance, absence of sweat production and dry skin, hyperpigmented periorbital skin.
Investigations Report:
CBC:
- Hb: 7.6g/dl
- ESR: 15mm in 1st hr
- TLC: 5500/cumm
- DC: N-42%, L-26%
- PLT-4,30,000cumm
- PBF: Moderate microcytic hypochromic anaemia
Serum Iron Profile:
- Iron-50µgm/dl
- Ferritin-18ng/dl
- Trasfrrin saturation-15%
- TIBC-500µgm/dl
- FT3: 4.37 pg/ml (N)
- FT4: 1.06 ng/dl (N)
- TSH: 1.56 µIU/ml (N)
- Vit -D: 8.2 ng/ml
- S.Calcium: 8.2mg/dl
- S.creatinine: 0.38mg/dl
So our final diagnosis is
Hypohydrotic Ectodermal dysplasia with vitamin D deficiency with iron deficiency anaemia
Treatment given as follows:
- Counselling about the nature and prognosis of the disease
- Maintain adequate hydration.
- Use light clothing.
- Avoid vigorous physical activity.
- Restrict exposure to warm temperatures.
- 7 years: Removable denture
- 18 years: Bone augmentation with permanent denture
- Syrup Compiron (Iron for IDA)
- Syrup Defrol OS (Vitamin D)
- Tablet Calbo Jr (Calcium supplement)
A consultation was done with the Skin department, and they advised Sonexa (Steroid) eye ointment Nyclobate (Steroid) scalp application Tablet Xinc B (Vitamin B complex with Zinc)
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial surgery gave advice for maxillary completion surgery followed by implantation of artificial dentures. They will implant permanent dentures at 18 years of age. The child is advised for regular follow-ups.
Discussion on Ectodermal Dysplasia
Ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia clefting syndrome (EEC syndrome) and also referred to as EEC syndrome and split hand–split foot–ectodermal dysplasia–cleft syndrome is a rare form of ectodermal dysplasia, an autosomal dominant disorder inherited as a genetic trait. EEC is characterized by the triad of ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia, and facial clefts. Other features noted in association with EEC include vesicoureteral reflux, recurrent urinary tract infections, obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, decreased pigmentation of the hair and skin, missing or abnormal teeth, enamel hypoplasia, absent punctae in the lower eyelids, photophobia, occasional cognitive impairment and kidney anomalies, and conductive hearing loss. Read more in Wikipedia or Download PDF Case report on EEC Syndrome
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Link
All ectodermal dysplasias are genetic disorders, which means that they can be passed on to children by parents. However, it is also possible for a child to be the first person in the family to be affected by ectodermal dysplasia. Learn more about genetics and inheritance of ectodermal dysplasia.
The National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias (NFED) is the worldwide expert on ectodermal dysplasias and the only advocacy organization in the United States dedicated to those living with these disorders.
Thanks, Everyone.



A comprehensive exploration of Ectodermal Dysplasia, offering valuable insights into this genetic condition. For a deeper understanding and additional information on Ectodermal Dysplasia, I highly recommend exploring detailed article at [ https://pharmacopathy.com/ectodermal-dysplasia-ed/ ]. It serves as a reliable resource, providing in-depth knowledge and guidance on managing this condition.